Java RPC协议设计
调用流程
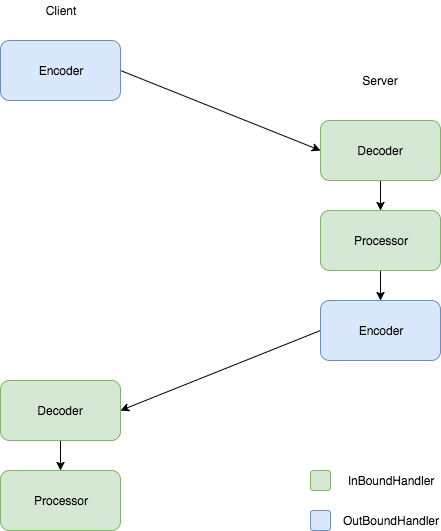
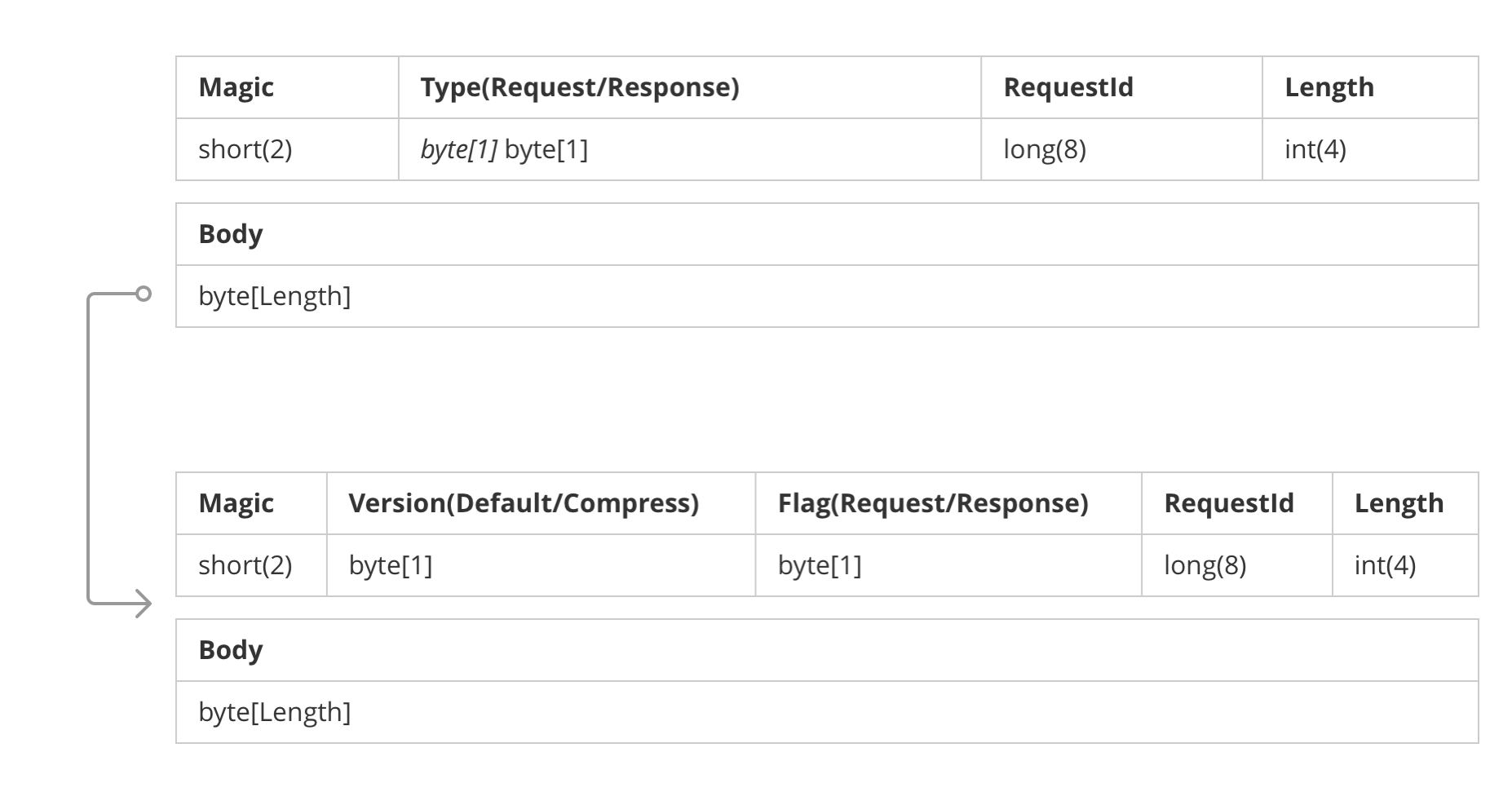
motan的协议设计
包括 request 级别的 header 和 body,request 的 body 中又包含了 header 和 body; 其中 requestId, request/response 的标记是冗余的
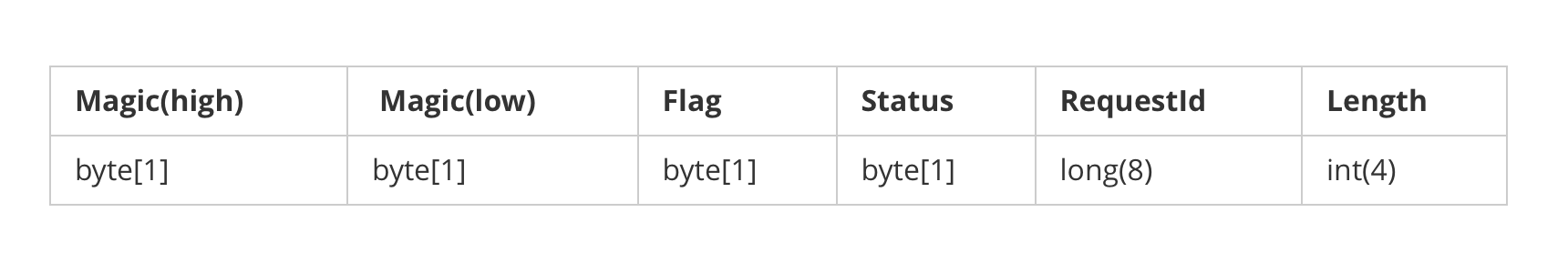
dubbo的协议设计
Server参数的优化
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128); // 3次握手连接队列
bootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true); // 默认false
bootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);Decoder

public class MessageDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf byteBuf, List<Object> list) throws Exception {
if (byteBuf.readableBytes() <= MessageConstant.HEADER_LEN) {
return;
}
byteBuf.markReaderIndex();
short type = byteBuf.readShort();
if (type != MessageConstant.MAGIC_TYPE) {
byteBuf.resetReaderIndex();
throw new Exception("error magic type");
}
byte messageType = (byte) byteBuf.readShort();
long requestId = byteBuf.readLong();
int dataLength = byteBuf.readInt();
if (byteBuf.readableBytes() < dataLength) {
byteBuf.resetReaderIndex();
return;
}
byte[] data = new byte[dataLength];
byteBuf.readBytes(data, 0, dataLength);
// debug
String r = new String(data, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(r);
list.add(new Message(r));
}
}
写的太简单了
王大神(王妈~),好久没写博客了喔~
在tool.lu的wiki和公司的学城里面写...